|
|
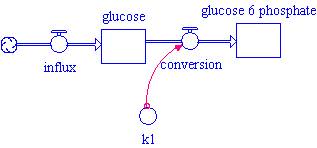 |
Kinetics: Mass action or Mass flux
Enzyme: glucose transporter, hexokinase (glucokinase)
System statements (disclaimers): ATP not taken into account.
| Reaction | Kinetics (Rate law) | Kinetic type | Constants | |
| Influx of Glucose | Facilitated diffusion | V Km |
||
| k | irreversible mass action | k | ||
| Conversion | Michaelis-Menten | V Km |
||
| k*Glucose | irreversible mass action | k |
Create the above model in Stella. Use the "Interface" window to attach sliders to the rate constant for hexokinase (k1) and glucose influx. Also add an input knob for the concentration of glucose. Set the range of values for the sliders and input knob to encompass the experimentally identified values given below in the parameter table. The input control knobs in Stella allow you to change the initial conditions of the simulation without having to open each object within the model.
| Parameter | Value mM/min | refs. | Value (Range) in Stella |
| Glucose transporter Vmax (k) |
0.0197 |
(15) (13) |
0.02- 55 |
| Hexokinase Vmax (k) | 0.84 51.7 68.5 242.8 |
(1) |
0.8- 240 |
| Km | 0.08 | (1) | NA |
| Variable | Concentration | (refs.) | Value Range in Stella |
| Glucose | 0.134 0.345 109 |
(15) (14) (13) |
0.1-110 |
| Glucose 6-phosphate | 1.011 1.51 |
(15) (1) |
1-1.5 |
Run a few simulations and discuss the results.
Sample worksheet for class assignment.