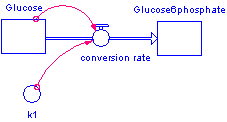
The following model is of the conversion of glucose to glucose 6-phosphate. The enzyme that mediates this reaction is hexokinase.

Questions to answer:
Initial Concentrations: For the reaction to occur there must be some amount of material, molecules or stocks.
Rate law: Stella must be told how to move stocks of glucose to glucose 6-phosphate. Since we are looking at enzymatic reactions, the "how" is commonly stated in the form of an enzymatic rate law. Enzymatic rate laws are also known as kinetic models.
Rate constant: k is the common notation for a rate constant. A rate constant is most often used in the rate law known as the law of mass action.
The results of a simulated model are a function of the structure of the model, the initial parameter values and the methods used to calculate the results. The linked page provides a series of simulation results. The structure of the model used to produce each result is the same.